Vaccine Manufacturing
Vaccine Manufacturing: Clinical Trials
Scientists around the world are continuously working on COVID Pandemic Vaccine Development; out of that, some vaccine markers are very close to accurate results. Around the world, more than 23 million Covid cases are found and 800,000+ deaths globally, Over the World more than 150 labs are constantly working on developing Covid-19 Vaccine. No one other than Russia has declared his vaccine is the safest vaccine over the Covid-19 pandemic. Apart from this vaccine development; the second largest problem to healthcare systems is, how to make this vaccine available to the global population at an affordable cost.
Clinical trials: Clinical trial is an investigation of a newly discovered drug on a human subject on a human subject, and reporting its safety and efficacy. It is carried out in the following ways
It is carried out in the following ways:
After successfully completing of Preclinical Phase, Vaccine go for the next Phase i.e. Clinical Phase. In Preclinical Phase we calculate our newly discovered drug effects on Preclinical Animal subjects like Rat, Mice, Monkey, etc.
In Clinical Trials, We use Human animals as subjects, wherewith the help of 4 phases, we calculate the efficacy and effectiveness of the product. Out of four, in Phase-I we ensure product safety & determine dosage on various age groups person from Pediatric patients to Gediatric patients; also ensure potential side effects of the newly discovered product but in very few people. In Phase-II we explore safety and investigate potential side effects on larger public groups. In Phase-III trials few more dosage manufactured and given them to thousand or up to ten thousands of people to access the effectiveness of the vaccine or newly discovered drug. There may be rare side effects that can only identify in large groups.
Four types of vaccines can be developed by using;
1. Whole virus
2. Protein subunit
3. Nucleic acids (RNA and DNA)
4. Viral vectors
1. Whole virus:
-most of the conventional vaccines use this mode.
-there may be two approaches viz,
i) Live Attenuated Vaccines.
ii) Inactivated Virus Vaccines.
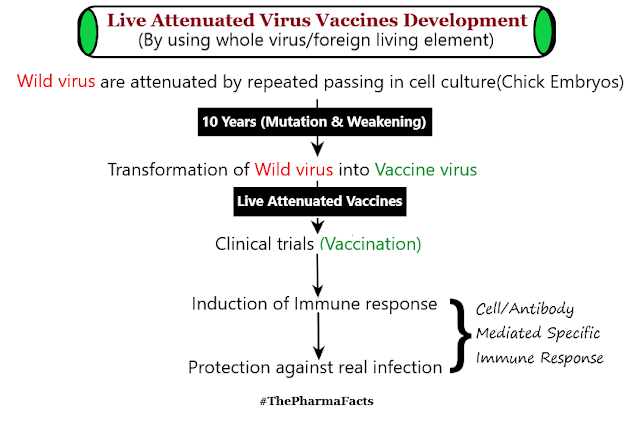
i) Live Attenuated Vaccines
-weakened form of viruses or foreign living elements that can still able to replicate without causing any harm or illnesses are used to develop this type of vaccine.
-these types of vaccines can provide both antibodies as well as cell-mediated immune response.
-Exa: Smallpox vaccine.
-shown in the figure below:
ii) Inactivated Vaccines
-the genetic material of viruses has been destroyed so that they can't replicate but still able to develop antibodies.
-these types of vaccines can only provide an antibody-mediated immune response.
-Exa: Poliovirus vaccine
Hepatitis A vaccine
-shown in the figure below:
2. Protein Subunit:
-these types of vaccines are designed by using species of pathogens.
-pieces of pathogens often fragments of protein to trigger an immune response.
-thus, the risk of side effects is minimized but the immune response may be weak and hence it requires adjuvant to boost the immune response.
-Exa: Hepatitis B vaccine
3. Nucleic Acid:
-these types of vaccines are established by using genetic materials like RNA or DNA of pathogens to provide instructions to cells for making antigens inside the host's body
-these are easy to make and cheaper in rate
-once these types of material interact with the host's body it produces antigens by using "Cell Protein Factories" and this helps to boost immunity.
-these vaccines provide strong immunity since antigens are formed inside the host's body.
-these vaccines are not allowed for human use.
4. Viral Vector:
-these also work in the same way as the nucleic acid derivative vaccines do by giving instructions to cells for producing antigens.
-they only differ from nucleic acid derivative vaccines in one way that viral vector vaccines are designed by using "Inactive virus" to give instructions for producing antigens in the host's body.
-mostly used inactive virus/viral vector is Adenovirus.
-these vaccines may be less effective if a viral vector is already exposed before the actual vaccination in the host's body but rather it could produce strong immunity.




Comments
Post a Comment
If you have any query or If you like the post,Please let me know.